The era where humanoid robots with shapes similar to humans are actively deployed in industrial sites is approaching. Recently, the American humanoid robot startup Aptronic secured $350 million in Series A funding to accelerate the commercialization of its AI-based humanoid robot ‘Apollo’. Google’s participation in this investment has increased the attention on the possibilities of the humanoid robot market.
Companies such as Tesla and Figure AI have already entered this field, and there are predictions that robots collaborating with humans will become key elements in transforming industries and society. However, this change might be a powerful factor that could fundamentally shake the structure of the labor market and economy beyond just technological innovation.
How far has the humanoid robot market come?
Unlike conventional industrial robots, humanoid robots are designed to mimic human body structures, allowing them to perform more complex tasks. ‘Apollo’, developed by Aptronic, stands at 173cm and weighs 72kg, possessing human-like proportions and is ready to be applied in various industries. It is expected to be used in fields with labor shortages such as logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare.
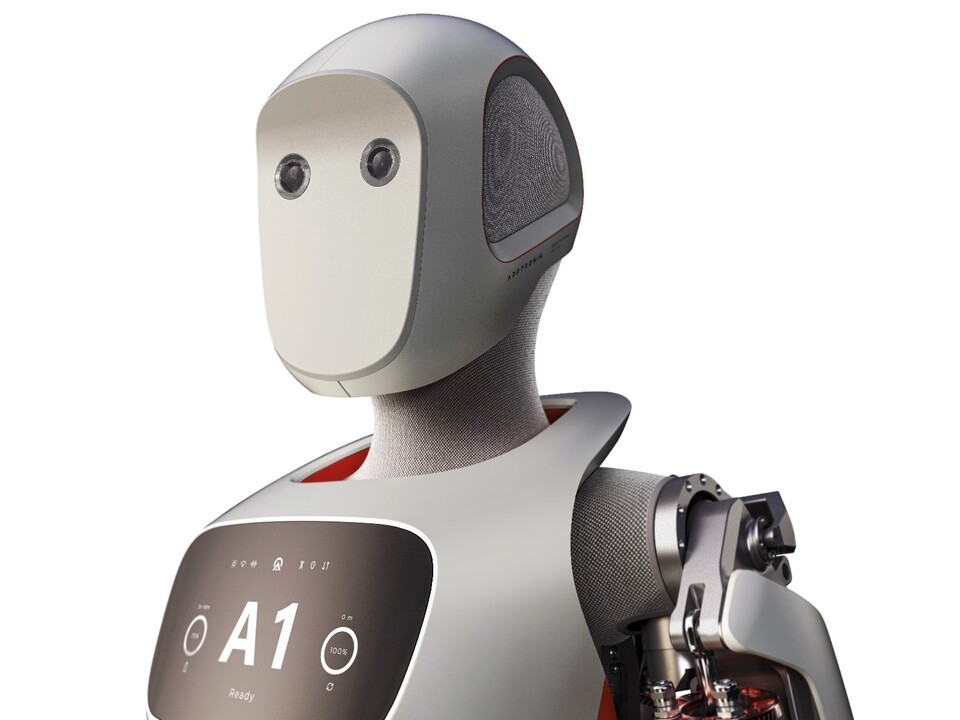

Particularly with the recent advancements in AI technology, the cognitive and decision-making abilities of humanoid robots have been rapidly improving. While they once could only perform simple repetitive tasks, robots with capabilities such as voice recognition, visual data analysis, and environmental adaptation are now emerging, thereby expanding their range of applications.
Tesla’s ‘Optimus’, Figure AI’s ‘Figure 01’, and Aptronic’s ‘Apollo’ are emerging as important variables set to reshape future industrial structures.
The economic and social impacts of humanoid robots’ spread
The most significant reason for the anticipation surrounding humanoid robots is the solution they provide to labor shortages.
Developed countries like the US, Europe, and South Korea are experiencing labor shortages due to low birth rates and aging populations. In particular, sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare face severe workforce shortages. The introduction of humanoid robots could increase productivity and reduce costs for businesses.
However, there is also significant concern about job reductions. As mechanization has replaced labor since the Industrial Revolution, warnings suggest that AI and robots will swiftly replace existing jobs. It’s not just simple manufacturing jobs but also service and clerical jobs that could potentially be affected.
Especially low-skilled workers might be the first to face impacts. If the roles of workers carrying products in warehouses or performing assembly tasks in factories are replaced by robots, there is a risk of increased polarization in the labor market. The global consulting firm McKinsey has projected that up to 800 million jobs could be automated globally by 2030.
Three strategies for coexistence between humans and robots
Before humanoid robots become widely distributed, we need to explore ways for humans and robots to coexist. To ensure that technological advancements lead to improvements in human quality of life, supporting policies and social preparations are crucial.
1. Establishing a new labor market model
Instead of replacing simple tasks with robots, humans need education and retraining to perform more creative and emotional roles. Rather than merely replacing simple labor, job structures should evolve to train personnel for managing and operating robots.
2. Considering the introduction of a robot tax
Some economists advocate for the introduction of a ‘robot tax’. When companies reduce labor by adopting robots, taxes can be levied for this and used for the retraining costs of laid-off workers.
3. Preparing ethical regulations for humanoid robots
If robots cause accidents, who bears legal responsibility? How can privacy be protected if robots perform surveillance and control functions? These issues need to be discussed in advance, and ethical standards for AI and robots should be reinforced.
Preparation for coexistence between robots and humans is necessary.
The emergence of humanoid robots is not a mere technological innovation. It represents a turning point that fundamentally changes the way humans perceive labor.
During the Industrial Revolution, machines replaced agriculture, and humans moved to cities to create new industries. Similarly, if an era comes where humanoid robots replace parts of labor, we must proactively seek ways to utilize this change.
The challenge ahead is to ensure technology becomes a tool that assists, rather than excludes humans. To ensure the future with humanoid robots is a hope rather than anxiety, social consensus and preparations are necessary from now on.