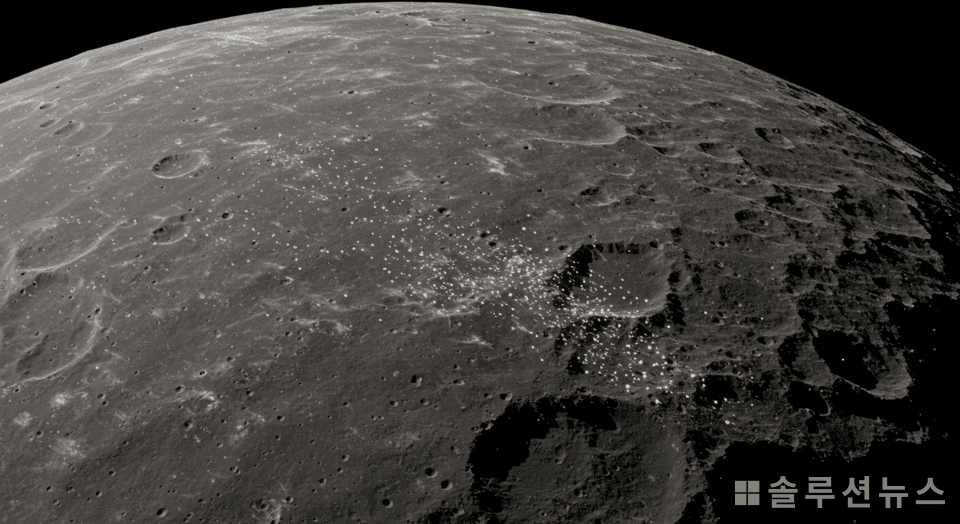
The presence of water on the moon, facilitated solely by the solar wind, has been proven.
A question long pondered by humanity has recently been answered by NASA researchers: Is there water on the moon? It has been officially confirmed through experiments that particles pouring from the sun can actually create water on the moon’s surface.
NASA announced this finding through the scientific journal JGR Planets on March 17, 2025. Dr. Li Hsia Yeo of the Goddard Space Flight Center, who led the study, stated, “Water can be created using only the basic materials of lunar soil and the sun.”
Unlike Earth, the moon lacks a magnetic field and atmosphere, leaving it exposed to high-speed particles emitted by the sun called solar wind. Hydrogen protons, the main component of the solar wind, collide with minerals on the moon’s surface, combining with oxygen to create hydroxyl (OH) and water molecules (H₂O). While the potential for such a scenario was previously suggested through lunar samples collected during the Apollo missions, this experiment is the first to practically demonstrate it.
The researchers used samples brought back by Apollo 17 in 1972. By heating the samples to remove moisture absorbed from Earth’s environment, they recreated lunar conditions in a laboratory by bombarding the samples with simulated solar wind particles. Using a high-speed particle accelerator, they generated short-term exposure equivalent to 80,000 years on the moon’s surface in just a few days.
The experiment detected a distinct light absorption signal near the 3-micrometer wavelength, a spectral response characteristic of the presence of hydroxyl or water, strongly suggesting the creation of water on the moon’s surface.
The water found on the moon’s surface does not remain static. Observations indicate that the moisture signals weaken during the day and strengthen at night, supporting the notion that solar wind continuously supplies hydrogen to the moon, perpetually creating water.
Aside from the solar wind, there are also studies suggesting that meteor impacts contribute to water creation. In 2016, NASA’s LADEE mission detected water molecules released in the lunar atmosphere during meteor showers. However, this study is significant in demonstrating that the solar wind itself is the primary source of water creation.
NASA’s achievement opens up the possibility in future Artemis missions to utilize not only the ice resources present in the moon’s South Pole region but also the water created by solar wind for sustained exploration.
Acquiring water on the moon goes beyond supplying drinking water; it plays an essential role in oxygen generation and fuel production, which are vital for maintaining lunar bases. This could prove to be a pivotal turning point in ushering in an era of space habitation.
What was once theoretical has now been validated as scientific fact through experimentation. Humanity can now view the moon not just as a “barren wasteland.”