Google has expanded the concept of artificial intelligence (AI) to another level. Previously, AI was limited to language and image-centered tasks like writing texts or drawing pictures. However, the newly unveiled ‘Gemini 2.5 Computer Use Model’, released by Google on the 7th (local time), is designed to go beyond merely generating information and enables AI to directly manipulate computer screens.
Google developed this model based on the visual recognition and logical reasoning capabilities of its AI platform, ‘Gemini 2.5 Pro’.
This model understands user commands and performs tasks by itself, such as clicking buttons or entering text on web pages or app screens. For example, it can fill out a website sign-up form, input data into a spreadsheet, and even schedule appointments in a reservation system.
Google introduced this model as a “new form of AI with faster and more accurate response speed than existing AI in both web and mobile environments.” Developers can use this feature through ‘Google AI Studio’ and ‘Vertex AI’ platforms.
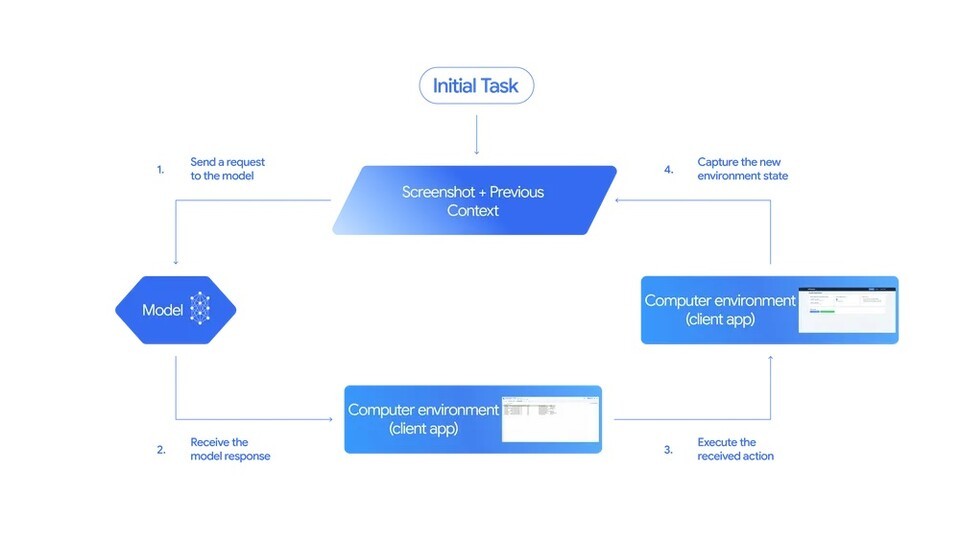
Unlike existing AI that mainly operated by exchanging data through ‘APIs’, a significant portion of actual digital tasks still requires humans to directly manipulate screens. Actions like entering information in a website input field and clicking a button to submit are examples of tasks that humans have to perform.
The ‘Gemini 2.5 Computer Use Model’ automates these processes. It receives a screenshot of the screen and records of the previous action along with the user’s request, analyzes the information, and determines “which button to click” or “what sentence to input”. The decision made by the AI is converted into commands like ‘click’, ‘input’, or ‘scroll’, and is executed on the actual screen.
Once the task is executed, the new screen is fed back into the model, and the process repeats until the goal is achieved. Google describes this as a “loop structure where the AI observes and acts repeatedly on the screen until the task is completed.” Whereas AI so far has been an entity that worked through language, this model is akin to AI equipped with ‘eyes and hands’.
Google claimed that the Gemini 2.5 Computer Use Model surpassed competing models in various benchmarks assessing web and mobile manipulation abilities. It achieved top rankings in major performance evaluations like ‘Online-Mind2Web’, ‘WebVoyager’, and ‘AndroidWorld’.
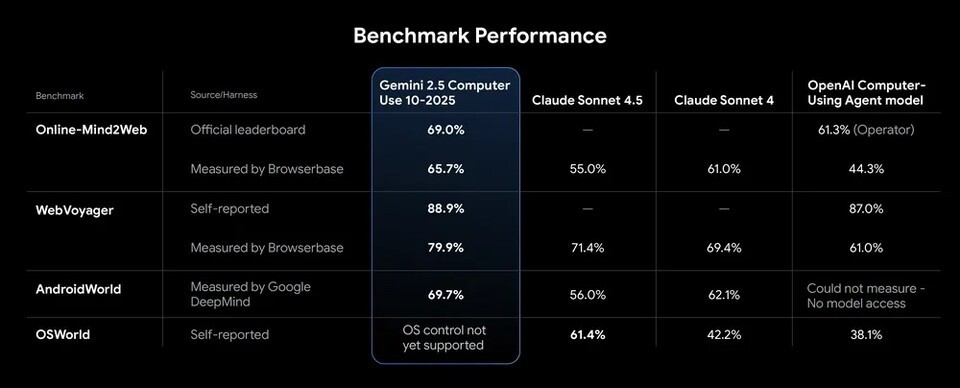
Especially in the Browserbase test, which measures web browser manipulation performance, it set the highest industry standards with over 70% accuracy and a latency of about 225 seconds, meaning it can manipulate the screen faster and more accurately for the same task. Google explained it as “the model with the highest browser control quality and the lowest latency.”
As AI directly manipulates computers, ensuring security and safety has become a crucial task. Google has embedded several safety features from the model’s design stage considering this issue.
First, a ‘per-step safety service’ has been applied to assess the risk of each action before the model performs it. This functionality evaluates whether the operation AI intends to execute could impact the system or pose a security risk, and blocks it if necessary.
Additionally, developers can use the ‘System instructions’ feature to restrict AI from automatically executing actions classified as high-risk, such as payments, security settings changes, and accessing personal information. Commands can be set to execute only after user confirmation if needed.
Furthermore, Google provides developers with security guidelines to ensure compliance with authentication procedures and data protection principles. The company stated, “The AI is designed to prevent unauthorized clicks on malicious links or changes to system settings in web environments,” emphasizing that “all developers must verify safety before deploying the actual service.”
Already experimentally used in Google’s internal system and external partner companies, the Gemini 2.5 Computer Use Model has shown significant results. Google’s payment platform development team applied it to UI tests, reducing past test failures by about 25%. Previously, correcting errors took days, but with AI’s capability to analyze and act on its own, the recovery rate has improved by more than 60%.
External partner Poke.com, a messaging-based AI assistant service, stated, “The work speed is 50% faster than competing models, and accuracy has also greatly improved.” Automation agent company Autotab also reported “performance was improved by 18% in complex data collection environments.”
Google began offering the Gemini 2.5 Computer Use Model as a preview starting today. Developers can test this feature directly through Google AI Studio and Vertex AI. They can also experience the process of AI actually clicking and entering data on a webpage in the demo environment provided by Browserbase.
Google stated, “AI has moved beyond simply understanding sentences and has now entered a stage where it manipulates actual screens and replaces human work.” The company plans to expand this technology into various industrial fields such as work automation, customer service, and test automation.
AI is transitioning from just ‘thinking’ like humans to ‘acting’ like them. The Gemini 2.5 Computer Use Model is not just a technical experiment, but technology opening a new phase where AI can directly manipulate the digital environments used by people daily. Routine digital tasks such as pushing buttons, entering information, and navigating the web are becoming increasingly automated. AI is no longer just an assistant but a colleague working alongside us.