The Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), headed by Vice Prime Minister and Minister Bae Kyung-hoon, announced on the 12th that it has achieved significant results in the production of diverse Carbon Capture Utilization (CCU) products such as fuel, chemical raw materials, and materials through continued research and development support in its role as the primary ministry in the field of CCU technology.
Carbon capture and utilization technology is the process of converting carbon dioxide into high-value products such as aviation fuel or methanol. South Korea has designated CCU as one of the 11 major sectors in its 2035 Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) goal for greenhouse gas reduction, with the MSIT leading the way in technology development and industry expansion.
The MSIT plans to increase the budget for CCU technology development and demonstration from KRW 29.6 billion in 2025 to KRW 64 billion in 2026, marking a 116% increase. It is also working on establishing a CCU technology and product certification system and a specialist company verification system, which reflects the opinions of experts from industry, academia, and research, thereby promoting greater industrial participation by private companies.
A demonstration project is underway in cooperation with four companies, including Hyundai Construction, to produce carbon dioxide conversion products such as liquefied carbon dioxide and dry ice. This project is expected to utilize approximately 30,000 tons of carbon dioxide annually, with the completion ceremony scheduled for October 2025.
This year, the MSIT is promoting the ‘CCU Mega Project,’ a large-scale demonstration project based on public-private cooperation. From 2026 to 2030, this KRW 380.6 billion project aims to overcome economic limitations and provide a foundation for industrial transformation by linking the supply of carbon dioxide to product production centered on high-emission industries.
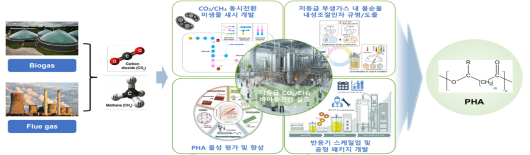
Thanks to continued government support, the MSIT has secured technology to produce chemical fuels and raw materials such as formic acid, lactic acid, methanol, and aviation fuel using carbon dioxide. It has also completed the transfer to the industry of production technologies for functional materials such as biodegradable polymers and bioplastics.
Technology transfers have been made to various companies including CNS Co., Ltd. (2026), Patek Co., Ltd. (2025), IntuKor Technology (2024), and LG Chem (2022).
Notably, the formic acid production technology developed by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) reduced the production cost from $790/ton to $490/ton and decreased carbon dioxide emissions by 42% compared to before. Formic acid is a basic chemical raw material used in industries such as leather tanning, dyeing, beekeeping, and livestock farming, where there was a high dependence on imports. However, domestic technology has improved both its economic and environmental viability.
The biodegradable polymer production technology developed by the Korea Institute of Energy Research has also lowered the cost to below $4/kg, increasing its commercial viability in a market where the current price range is $4 to $7/kg.
The MSIT is extending its support to include technologies that produce high-value compounds such as glutamic acid, formaldehyde, and methyl formate using carbon dioxide. It is also conducting demonstrations of technologies that produce crude oil using carbon dioxide and hydrogen. This technology aims to demonstrate daily production of 900 kg (300 tons annually) of crude oil by 2030, with the expectation of converting 3 million tons of carbon dioxide into 900,000 tons of crude oil by 2040.
Oh Dae-hyun, Director of Future Strategic Technology Policy at the MSIT, stated, “Carbon capture and utilization technology is a core technology for achieving carbon neutrality and an innovative technology that creates resources that could not previously be produced domestically. We will support the CCU industry to further advance beyond laboratory levels to a stage where it can be directly applied in industrial settings.”