The Ministry of Science and ICT on the 27th (Thursday) conducted a survey to assess the national perception of the results of the digital inclusion policy and announced the findings to actively respond to changes in the policy environment following the enactment of the ‘Digital Inclusion Act’ in 2024.
This survey is a national approved statistic that measures the digital information level of digitally vulnerable groups (low-income earners, people with disabilities, farmers and fishermen, the elderly, etc.) compared to the general public to understand the gap in digital access, capability, and utilization levels.
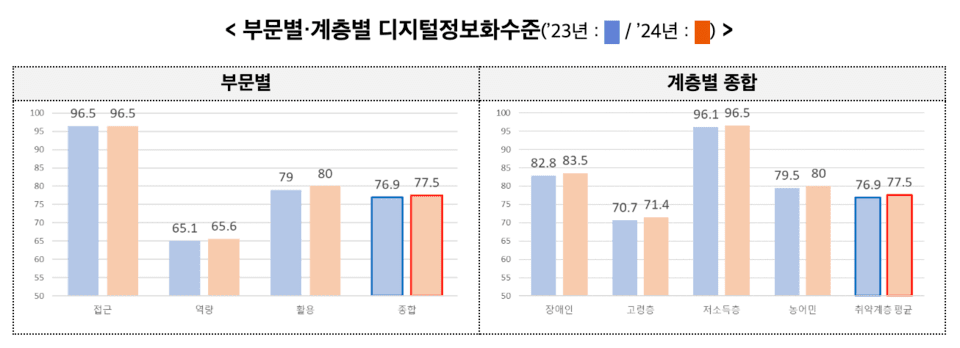
According to the digital divide survey results, the information level of vulnerable groups was found to be an average of 77.5%, which is an increase of 0.6 percentage points compared to the previous year and has shown a steady upward trend over the past five years. By sector, digital access level was 96.5%, capability level was 65.6%, and utilization level was 80.0%.
By group, the elderly scored 71.4%, farmers and fishermen 80.0%, people with disabilities 83.5%, and low-income earners 96.5%, with improvements in the information level for all groups compared to the previous year. The survey methodology calculates indices by comprehensively assessing digital accessibility, device utilization ability, and actual service utilization.
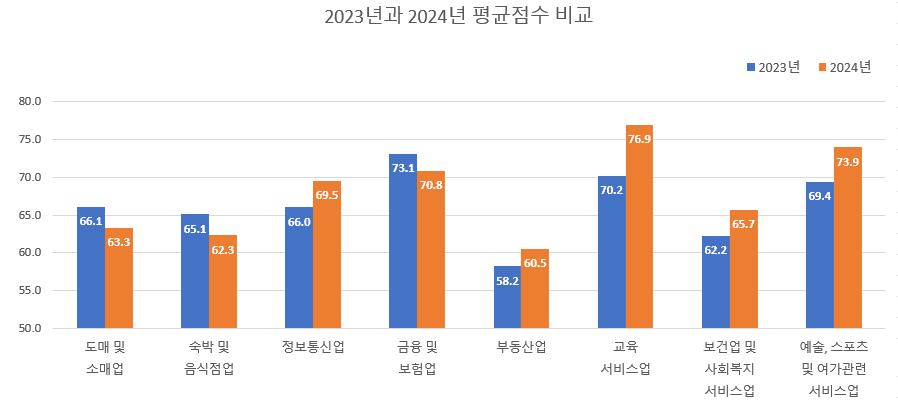
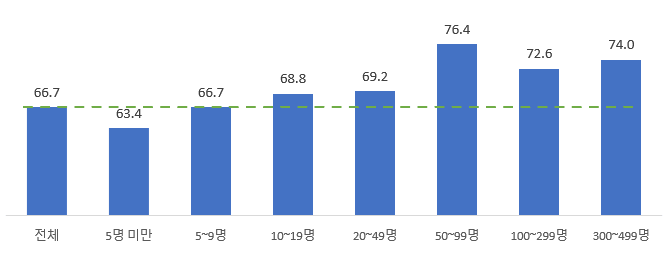
The web accessibility survey was conducted by randomly extracting 1,000 websites in eight industries with high web usage frequency. The overall average score was 66.7 points, an increase of 0.9 points from 2023. The educational services industry had the highest score of 76.9 points, while the real estate industry had the lowest at 60.5 points. By size, companies with 50 to 99 employees had the best web accessibility.
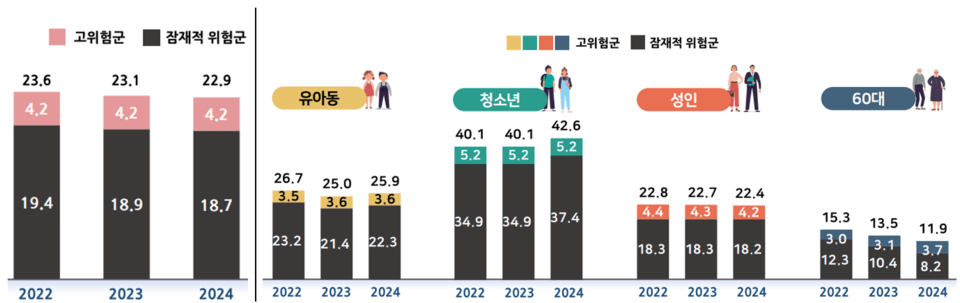
The smartphone dependency survey examined the smartphone usage patterns of citizens through 1:1 interviews across 10,000 households in 17 regions nationwide.
In 2024, the percentage of smartphone users in South Korea classified as at risk for over-dependence was 22.9%, a decrease of 0.2 percentage points from the previous year. However, it increased by 2.5 percentage points for teenagers (aged 10 to 19) and by 0.9 percentage points for young children (aged 3 to 9). For adults (aged 20 to 59) and the elderly over 60, it decreased by 0.3 percentage points and 1.6 percentage points, respectively.
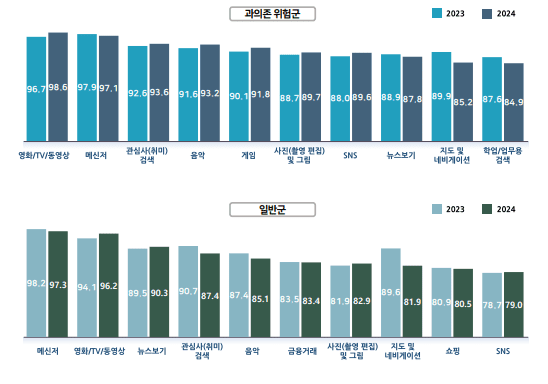
Examining the usage patterns of different content, the over-dependence risk group showed high utilization rates in the order of movies, TV, videos, messengers, search, and music. In contrast, general users showed a preference for messengers, movies, TV, videos, news, and interest-based searches.
This survey was conducted through interviews and web accessibility tests by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Information Society Development Institute, and the results can be checked on the relevant ministries’ websites.